reading-notes
Django CRUD and Forms
Readings
Notes
Creating forms using built-in form classes such as CharField and EmailField
Django provides several built-in form classes such as CharField, EmailField, and ChoiceField that can be used to create forms. These classes can be imported from the django.forms module and used to create form fields.
Customizing form fields by setting attributes such as label and widget
Form fields can be customized by setting attributes such as label and widget. The label attribute is used to set the text that appears next to the form field, and the widget attribute is used to set the type of widget that should be used to display the field (e.g. text input, select box, etc.).
Creating custom form classes by inheriting from forms.Form or forms.ModelForm
Custom form classes can be created by inheriting from forms.Form or forms.ModelForm. forms.Form is used to create forms that do not have a corresponding model, while forms.ModelForm is used to create forms that are based on a specific model.
Handling form submission and validation by using the is_valid() method and accessing cleaned_data
When a form is submitted, it can be validated using the is_valid() method. If the form is valid, the cleaned_data attribute can be accessed to retrieve the data from the form.
Rendering forms in templates by using form.as_p, form.as_table, or template tags
Forms can be rendered in templates using template tags such as form.as_p, form.as_table, or . These tags can be used to generate the HTML markup for the form.
Using forms in views by passing them to the context and displaying them in templates
Forms can be used in views by passing them to the context and displaying them in templates. For example, a form can be created in a view, passed to the context, and then displayed in a template using the template tags described in the previous point.
Using forms for creating, updating, and deleting models using ModelForm
forms.ModelForm is used to create forms that are based on a specific model. This class can be used to create forms for creating, updating, and deleting models. The forms can be used to validate and save data to the models.
Django Form Handling Process
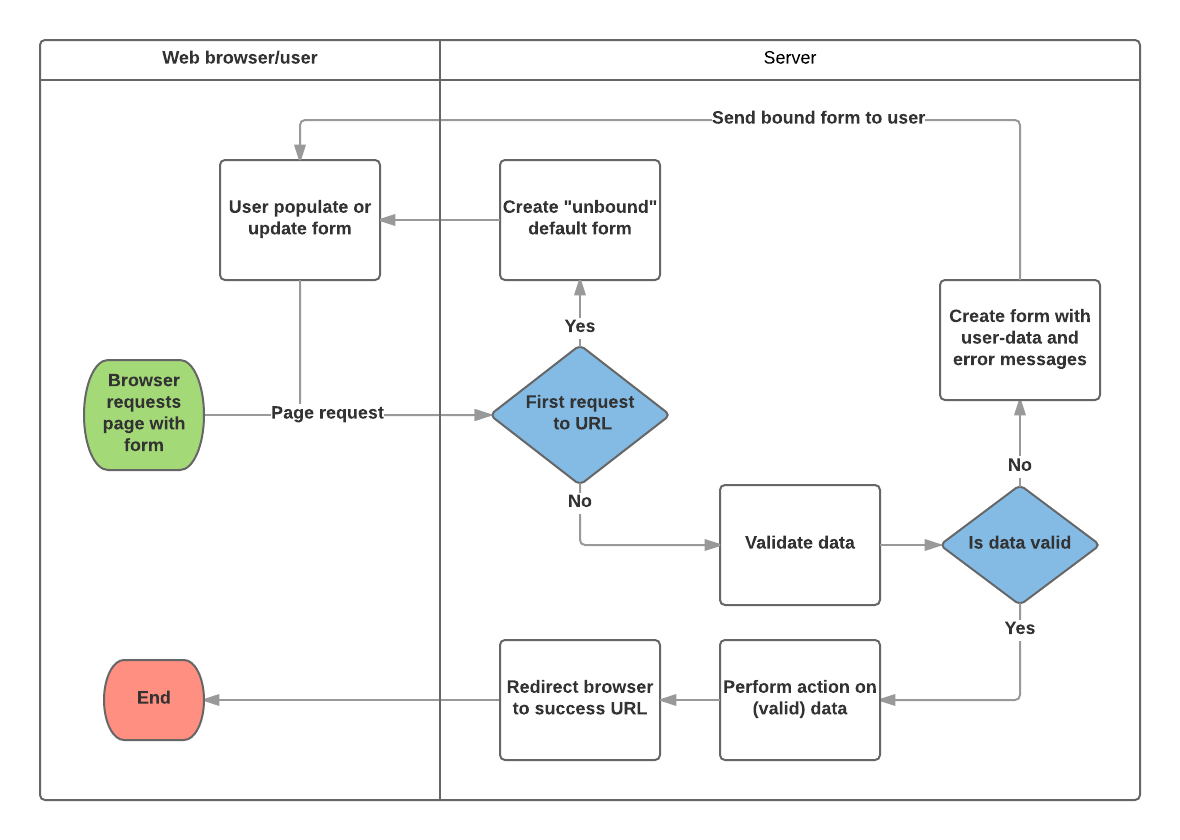
Using Forms in Django
- Creating a form using built-in form classes
from django import forms
class ContactForm(forms.Form):
name = forms.CharField(label='Your Name')
email = forms.EmailField(label='Your Email')
message = forms.CharField(widget=forms.Textarea)
- Customizing the fields of a built-in form
class ContactForm(forms.Form):
name = forms.CharField(label='Your Name', widget=forms.TextInput(attrs={'class': 'my-custom-class'}))
email = forms.EmailField(label='Your Email', required=False)
message = forms.CharField(widget=forms.Textarea)
- Creating a custom form class that inherits from
forms.ModelForm
from django import forms
from .models import MyModel
class MyModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = MyModel
fields = ['field1', 'field2']
- Handling form submission and validation
def my_view(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = ContactForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
name = form.cleaned_data['name']
email = form.cleaned_data['email']
message = form.cleaned_data['message']
# Do something with the data
return HttpResponseRedirect('/success/')
else:
form = ContactForm()
return render(request, 'my_template.html', {'form': form})
- Rending forms in templates
<form method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
- Using forms in views
def my_view(request):
form = ContactForm()
return render(request, 'my_template.html', {'form': form})
- Using forms for creating, updating, and deleting models (CRUD operations)
def create_model(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = MyModelForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect('/success/')
else:
form = MyModelForm()
return render(request, 'create_model.html', {'form': form})