reading-notes
Stacks and Queues
Readings
Notes
Stacks
- What is a stack?
- A data structure that consists of
Nodes - Each
Nodereferences the nextNodein the stack, but not the previous
- A data structure that consists of
- Stack Terminology
- Push - Nodes or items that are put into the stack are pushed
- Push = added to the stack
- Pop - Nodes or items that are removed from the stack are popped. When you attempt to pop an empty stack an exception will be raised.
- Pop = remove from the stack
- Top - This is the top of the stack.
- Peek - When you
peekyou will view the value of the top Node in the stack. When you attempt topeekan empty stack an exception will be raised. - IsEmpty - returns true when stack is empty otherwise returns false.
- Push - Nodes or items that are put into the stack are pushed
- Stack Concepts
- First In Last Out
- First item added to the stack is the last item popped out of the stack
- Last In First Out
- The last item added to the stack is the first item popped off the stack
-
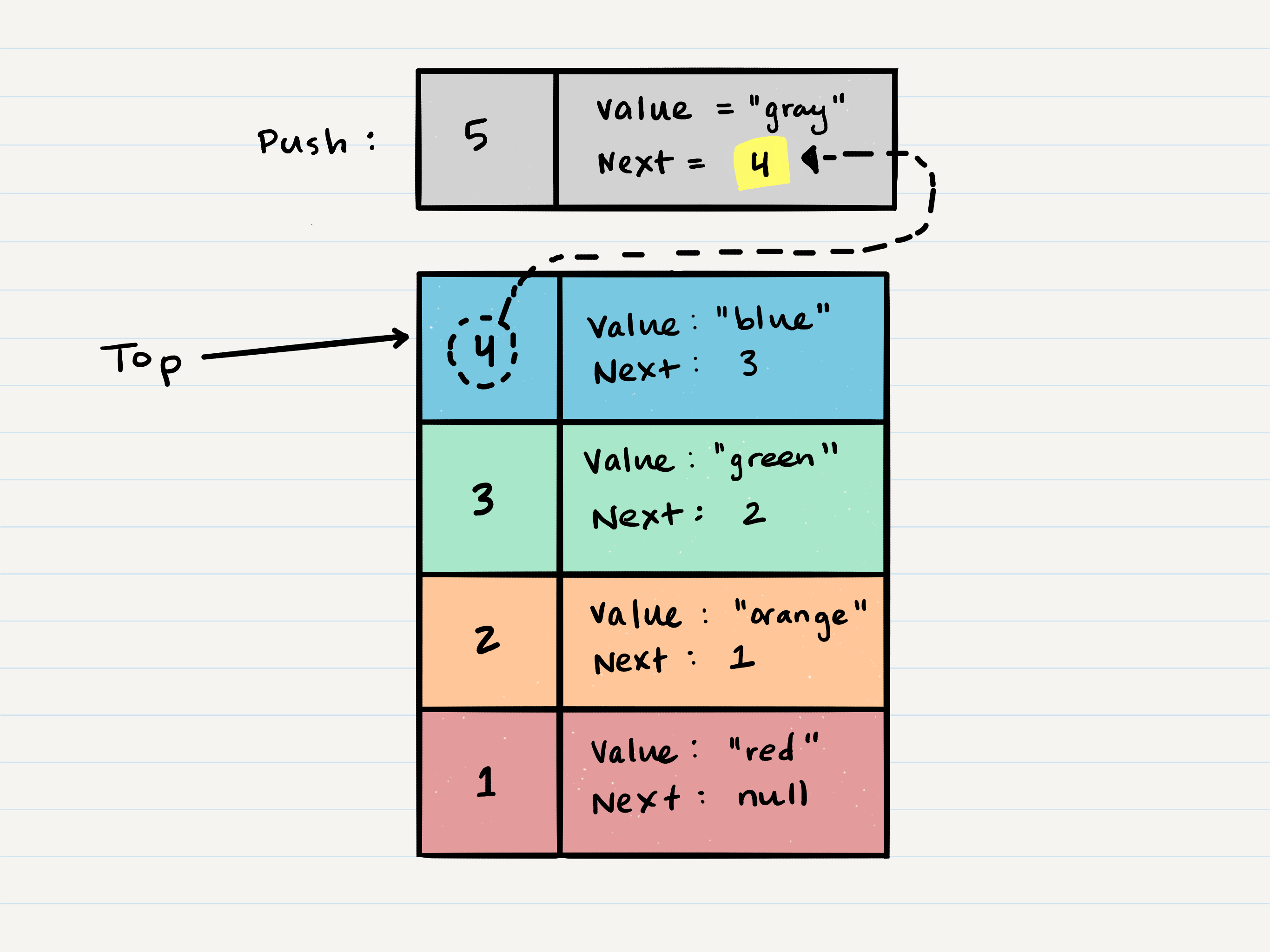
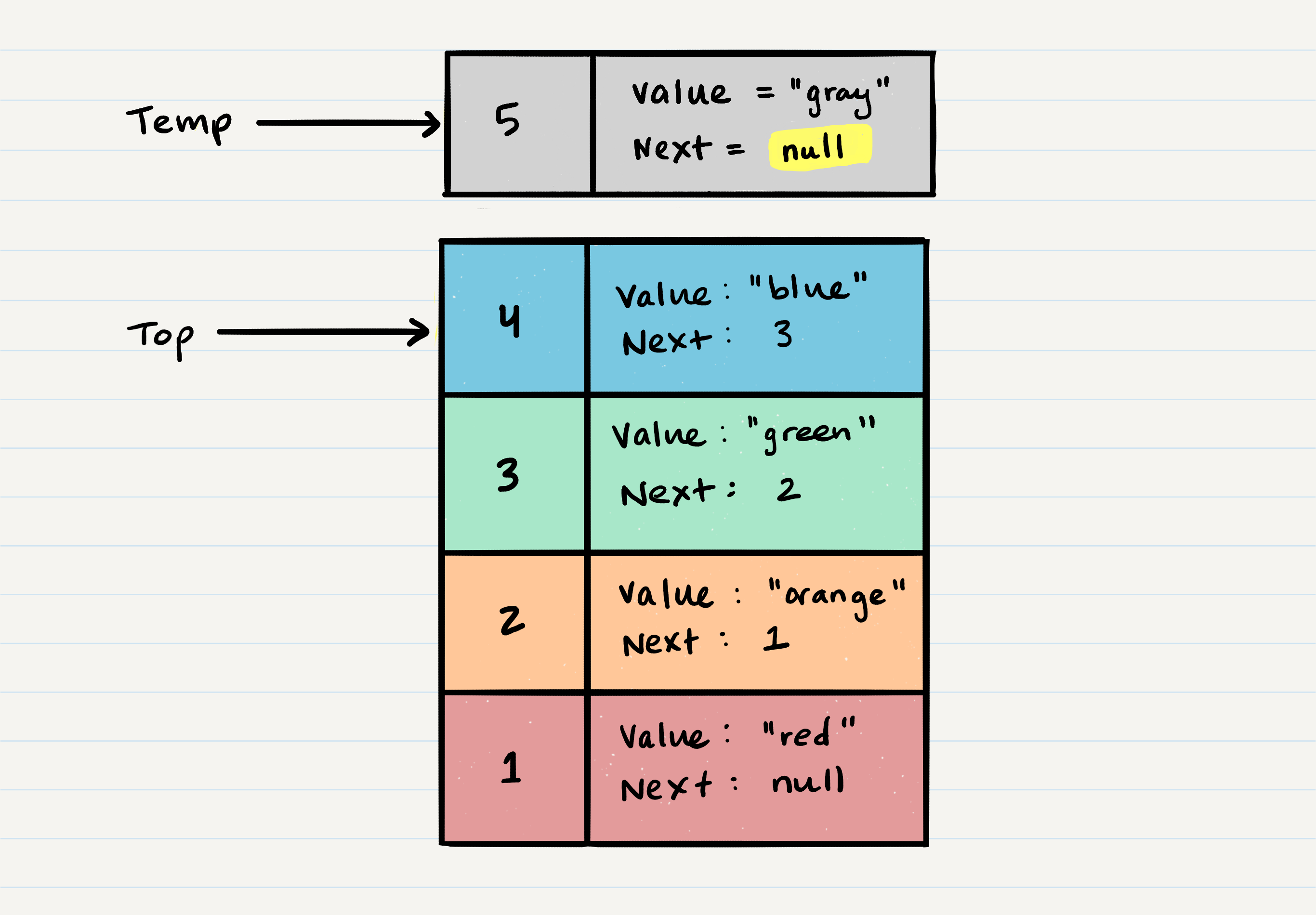
Stack Visualization
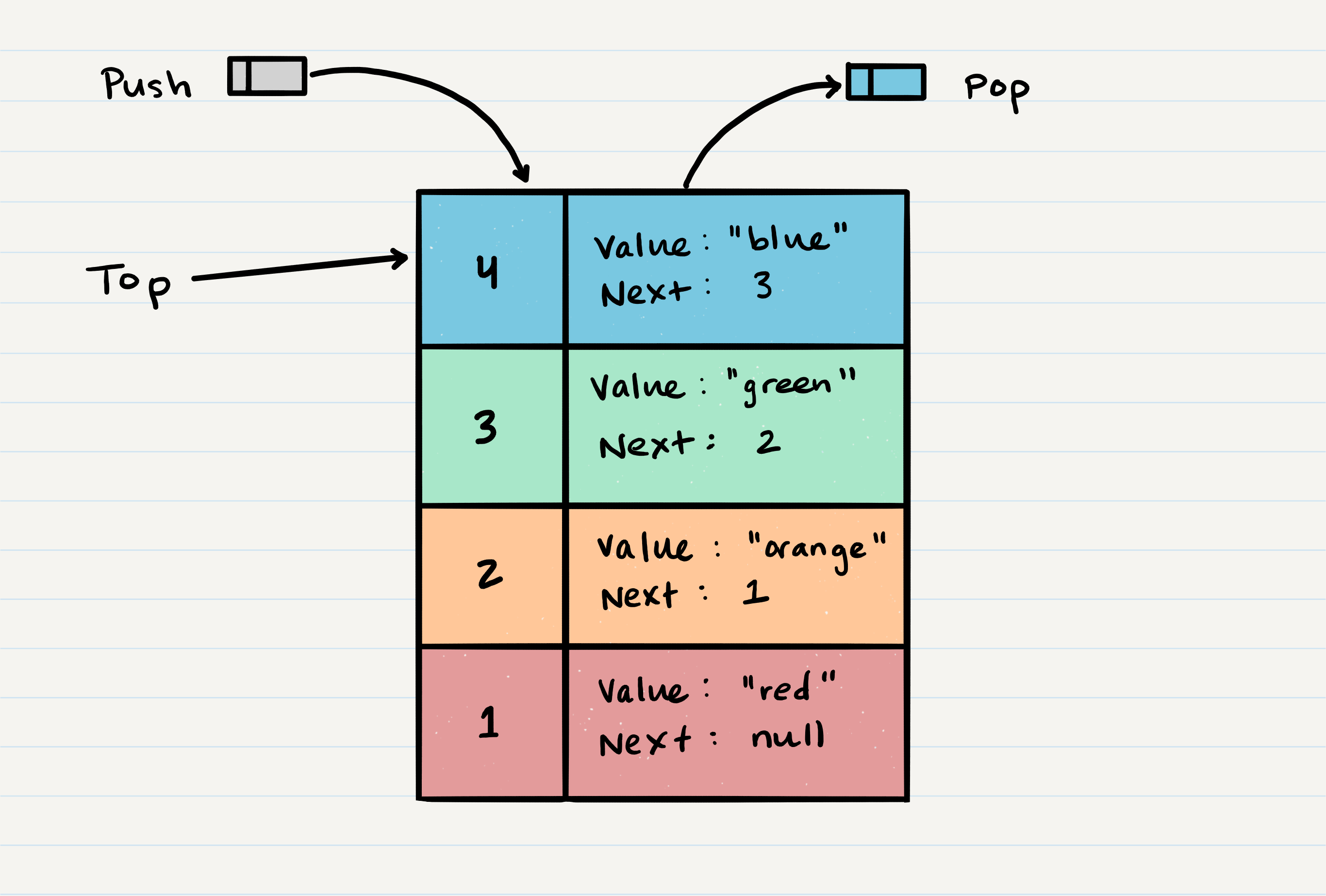
- The topmost item it denoted as
top - When you
pushsomething to the stack, it becomes the newtop - When you
popsomething off the stack, you remove the currenttopand set the nexttopastop.next
- The topmost item it denoted as
- First In Last Out
- Stack Operation Details
- Push
- O(1)
- Always takes the same amount of time no matter how many
Nodesare in the stack since you are always pushing to the top of the stack
- Always takes the same amount of time no matter how many
- When adding a
Node, youpushit to the stack by assigning it as the newtopwith itsnextproperty equal to the oldtop - Steps
- Connect the new
topto the oldtopby setting thetop.nextproperty to equal the oldtop - Assign the
topvalue equal to the value of the newNode
- Connect the new
-
Code example
ALOGORITHM push(value) // INPUT <-- value to add, wrapped in Node internally // OUTPUT <-- none node = new Node(value) node.next <-- Top top <-- Node
- O(1)
- Pop
- O(1)
- Always takes the same about of time to
popa node off the stack since you are always removing one off the top of the stack
- Always takes the same about of time to
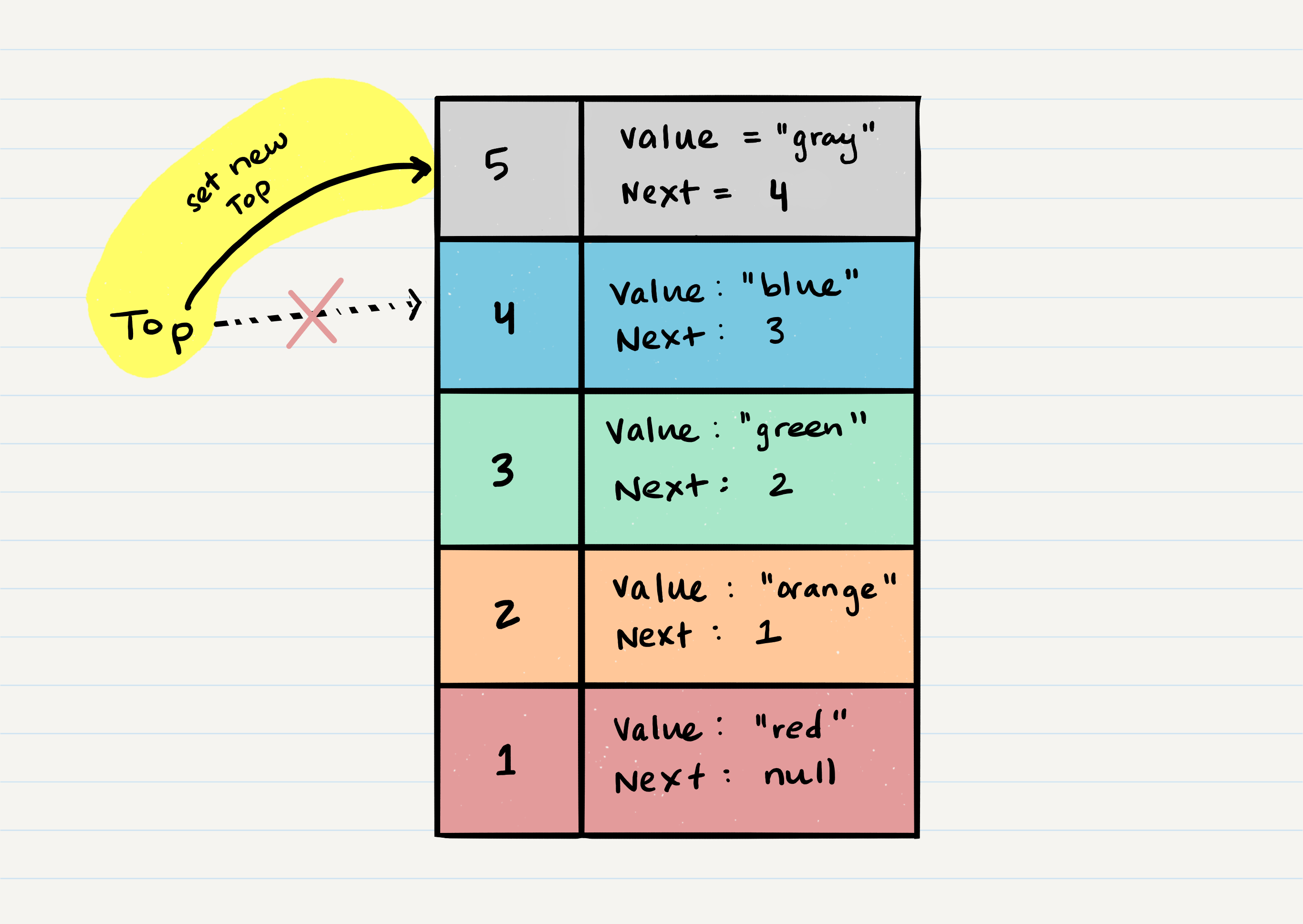
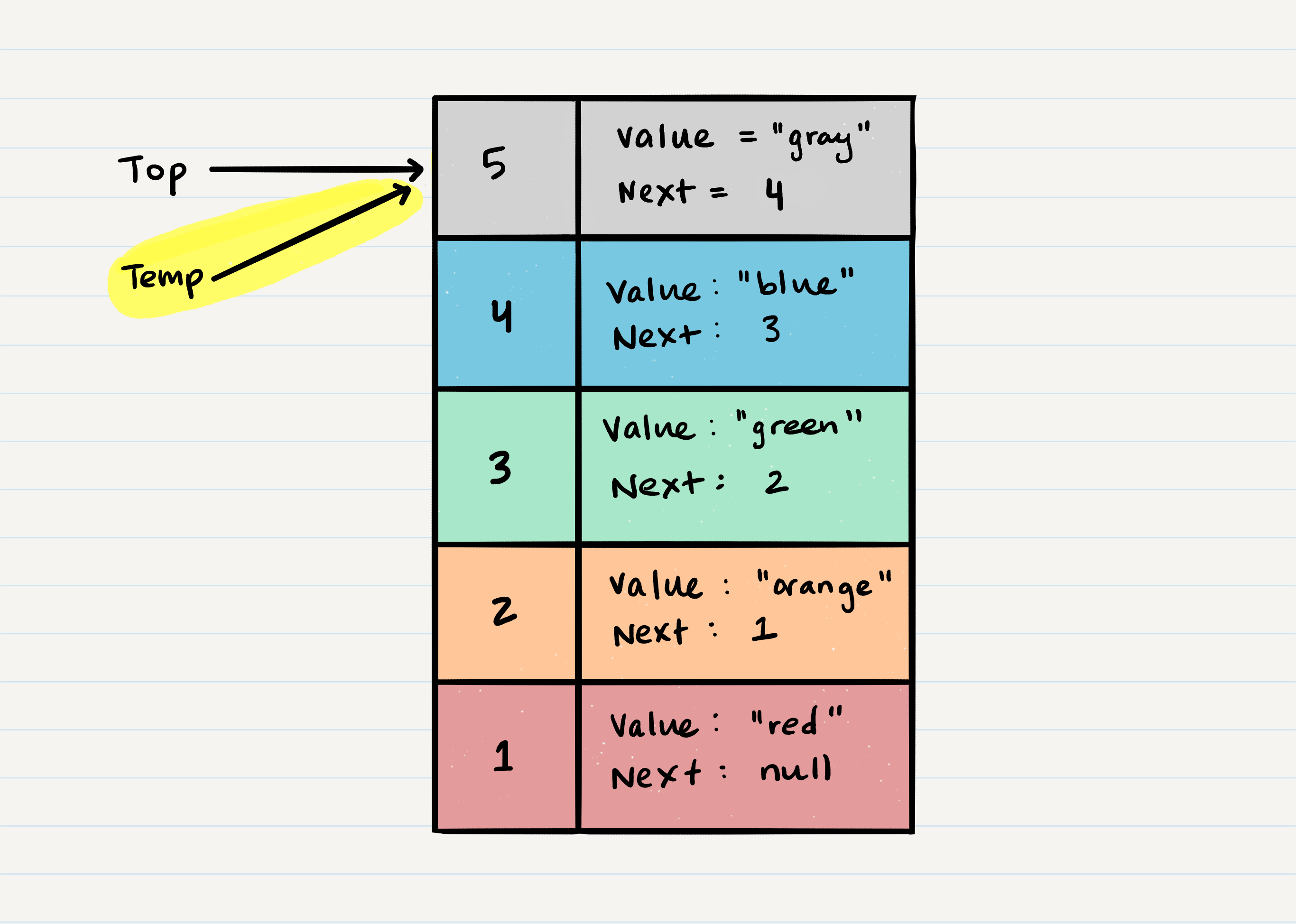
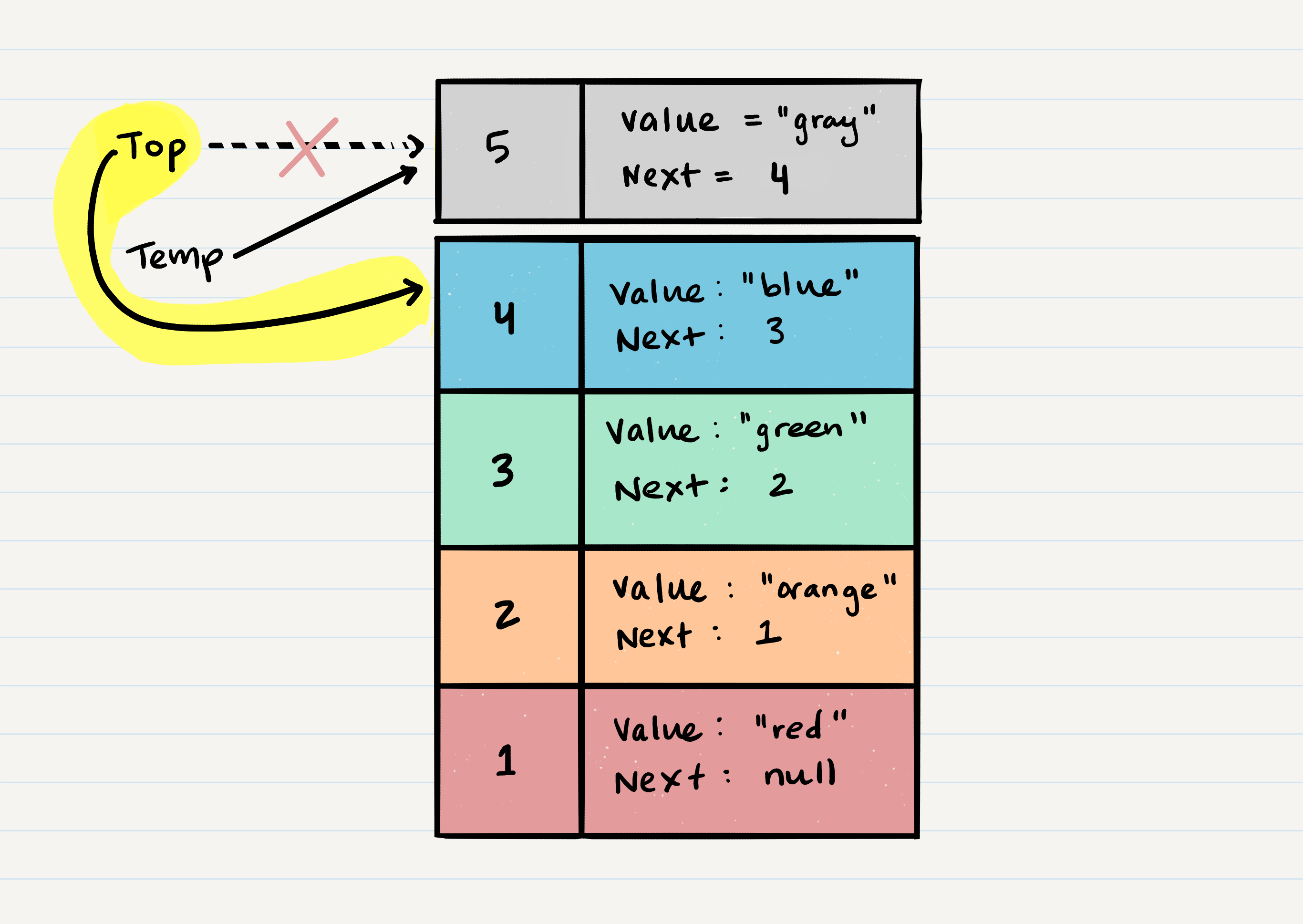
- When you
popaNodeoff the stack, first you checkisEmptyto ensure no exception is raised, then you set atempvariable to hold the oldtop, then you assign the value oftopto the value that thenextproperty is referencing, then you clear thenextreference in thetempvariable, then returntempto the user - Steps
- Create a
tempvariable and assign the currenttopto it - Assign the
topvalue to thetemp.nextproperty - Clear out the
nextproperty in thetempvariable - Return
tempto the user
- Create a
-
Code example
ALGORITHM pop() // INPUT <-- No input // OUTPUT <-- value of top Node in stack // EXCEPTION if stack is empty Node temp <-- top top <-- top.next temp.next <-- null return temp.value
- O(1)
- Peek
- O(1)
peekonly looks at thetopNode of the stack
- Looks inside and returns
top.valueif the stack is not empty -
Code example
ALGORITHM peek() // INPUT <-- none // OUTPUT <-- value of top Node in stack // EXCEPTION if stack is empty return top.value
- O(1)
- IsEmpty
- O(1)
- Code example
ALGORITHM isEmpty() // INPUT <-- none // OUTPUT <-- boolean return top = NULL
- Push
Queues
- What is a queue?
- First In First Out, Last In Last Out data structure
- Queue Terminology
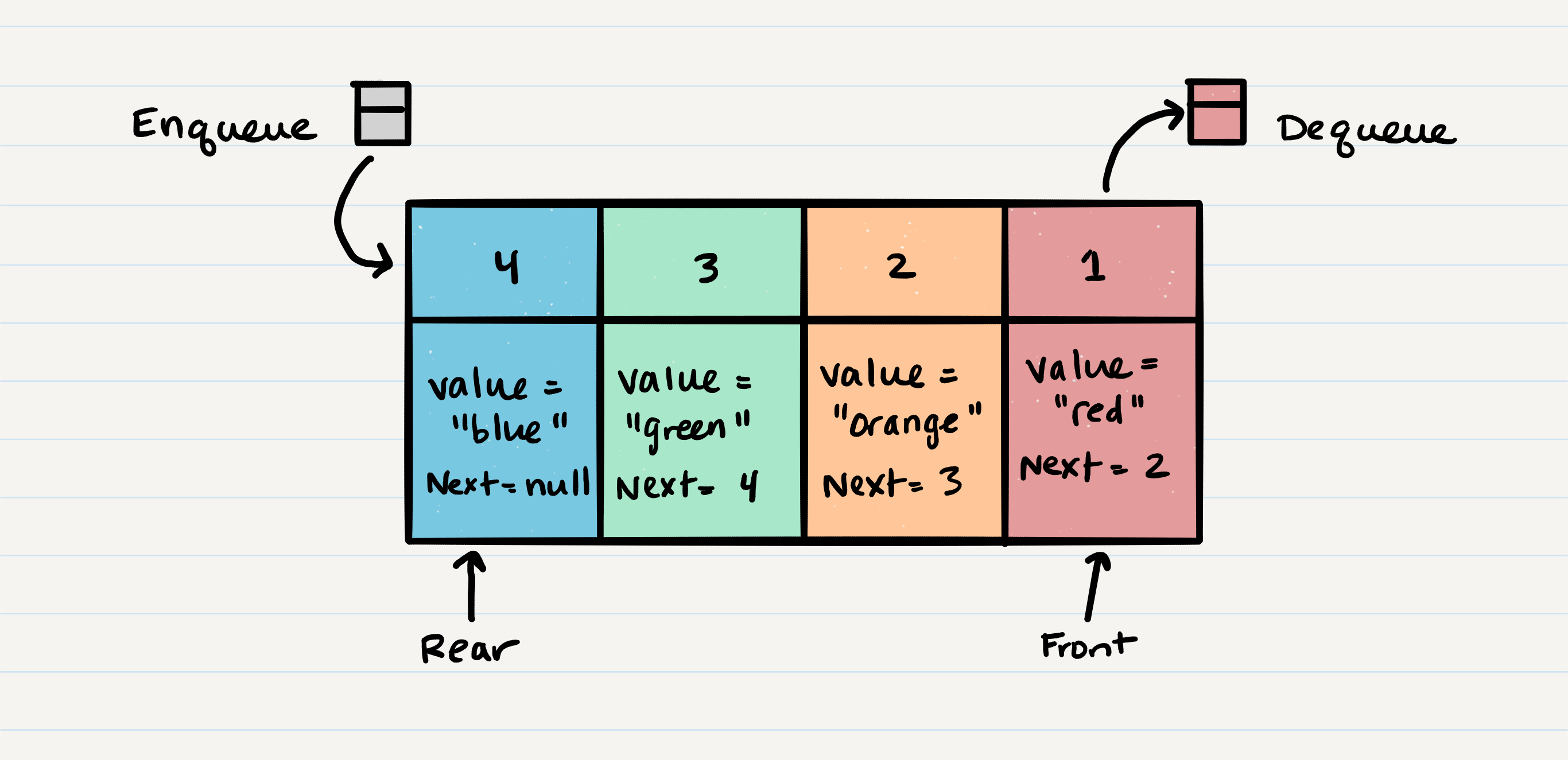
- Enqueue - Nodes or items that are added to the queue.
- Dequeue - Nodes or items that are removed from the queue. If called when the queue is empty an exception will be raised.
- Front - This is the front/first Node of the queue.
- Rear - This is the rear/last Node of the queue.
- Peek - When you
peekyou will view the value of thefrontNode in the queue. If called when the queue is empty an exception will be raised. - IsEmpty - returns true when queue is empty otherwise returns false.
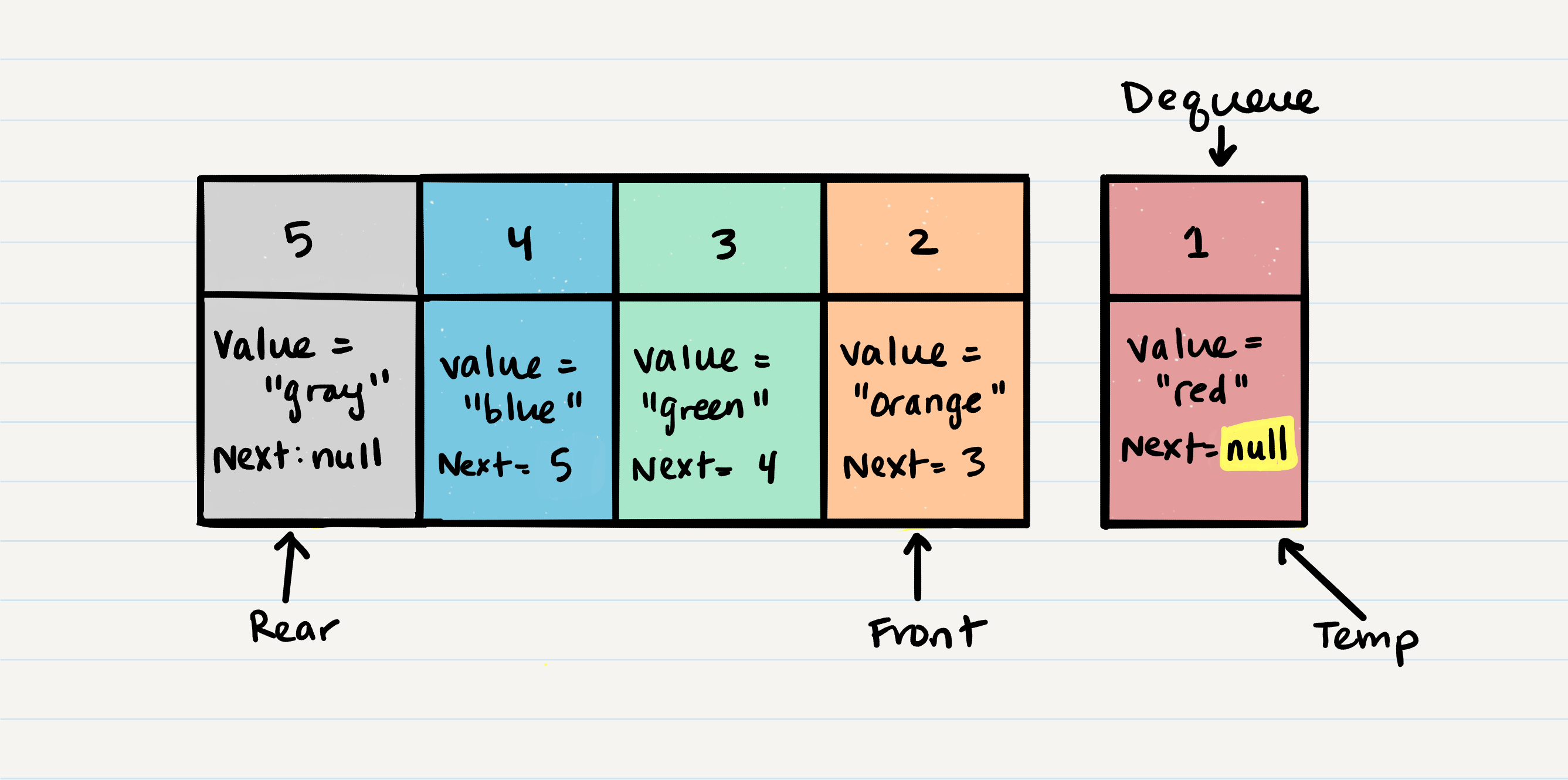
- Queue Visualization
- Queue Operations
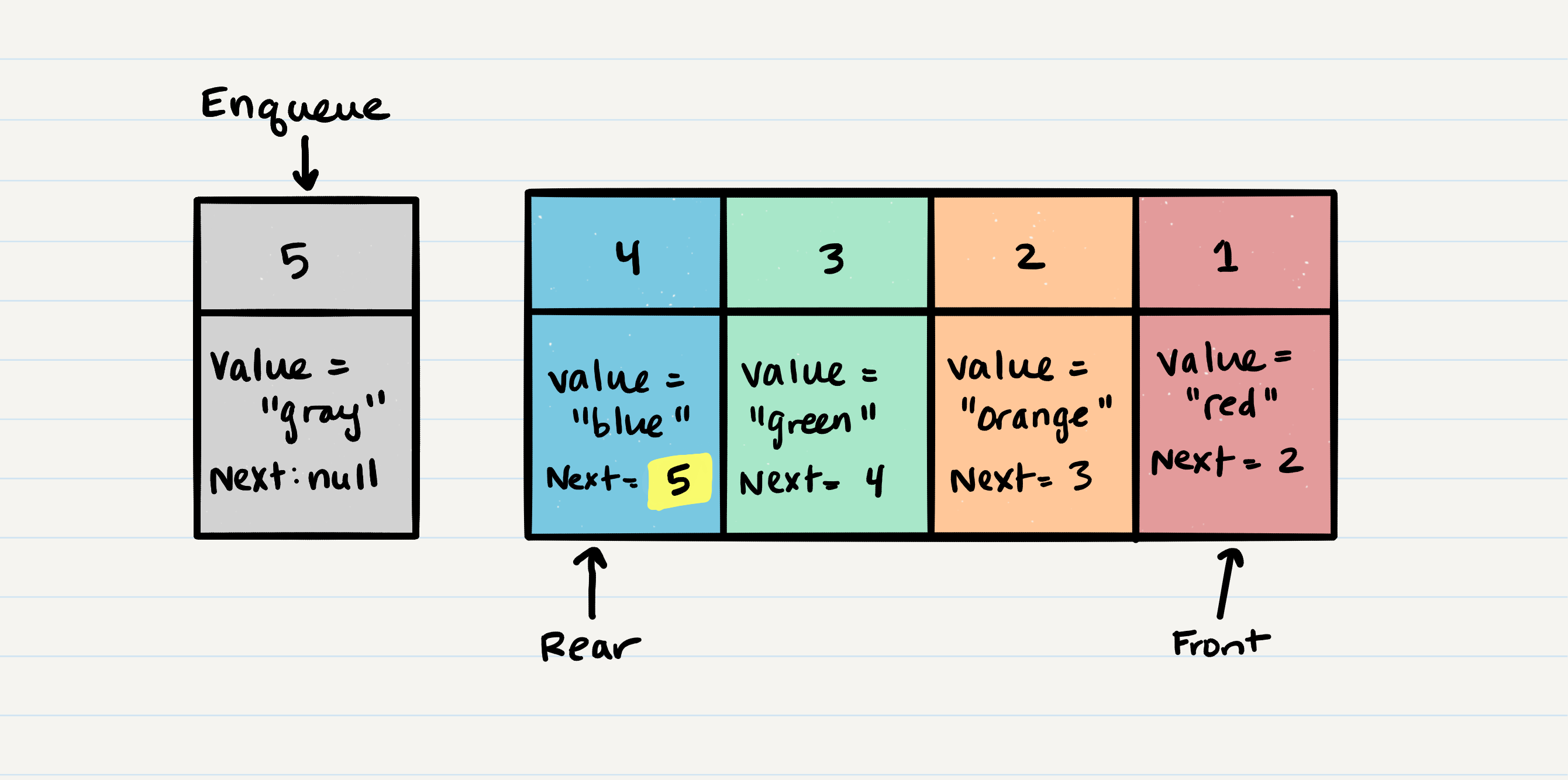
- Enqueue
- O(1)
- Adds item to the back of the queue
- Steps
- Assign the
nextproperty of the last Node in the queue to the value of the new Node
- Assign the
-
Code example
ALGORITHM enqueue(value) // INPUT <-- value to add to queue (will be wrapped in Node internally) // OUTPUT <-- none node = new Node(value) rear.next <-- node rear <-- node
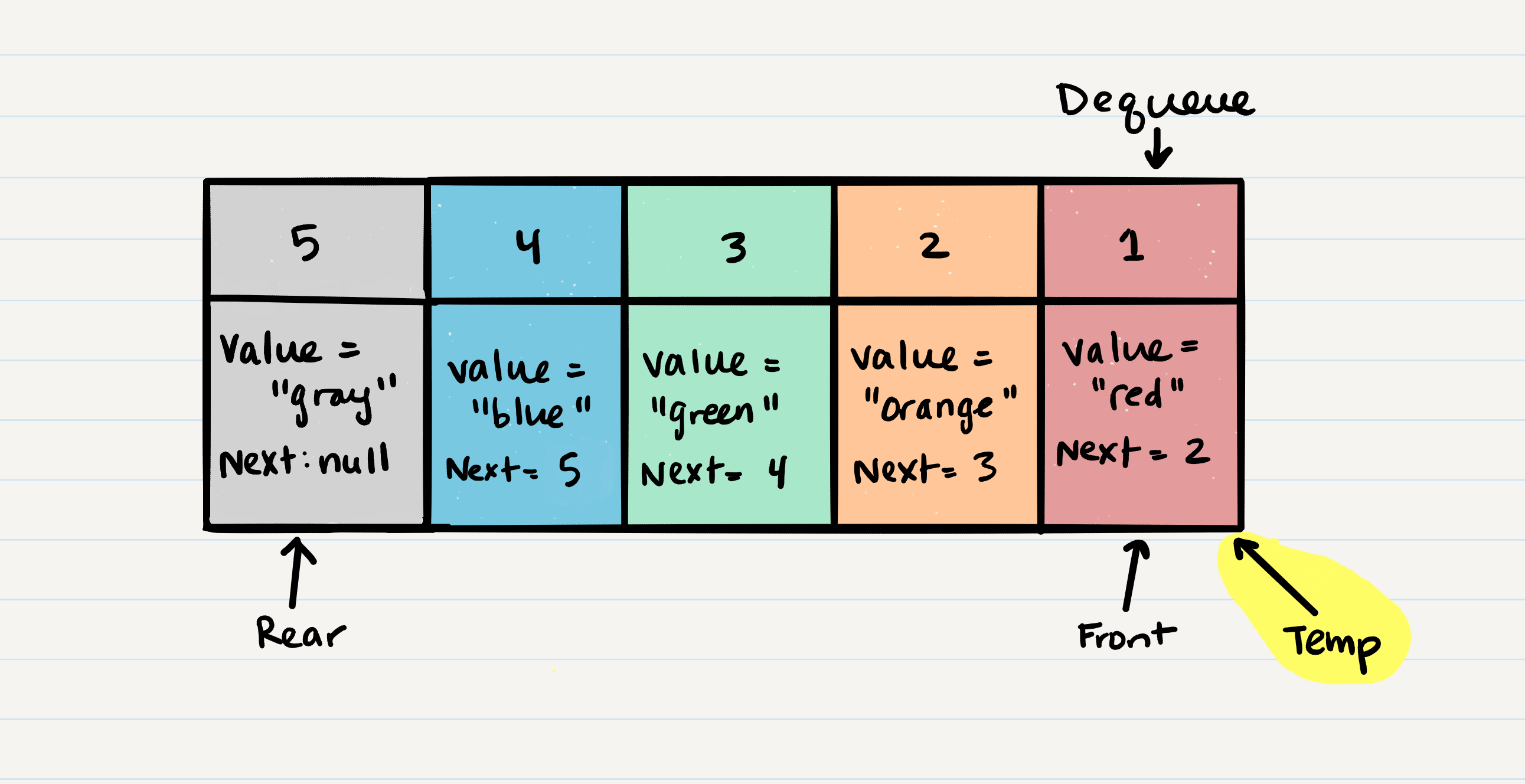
- Dequeue
- O(1)
- Removes item from front of queue and returns it to the user
- Steps
- Create a
tempvariable and assign front Node to it - Clear the
temp.nextattribute and returntempto the user
- Create a
-
Code Example
ALGORITHM dequeue() // INPUT <-- none // OUTPUT <-- value of the removed Node // EXCEPTION if queue is empty Node temp <-- front front <-- front.next temp.next <-- null return temp.value
- Peek
- O(1)
- Inspects the
frontnode and returns its value -
Code example
ALGORITHM peek() // INPUT <-- none // OUTPUT <-- value of the front Node in Queue // EXCEPTION if Queue is empty return front.value
- IsEmpty
- O(1)
- Checks to see if queue is empty and returns a boolean
-
Code example
ALGORITHM isEmpty() // INPUT <-- none // OUTPUT <-- boolean return front = NULL
- Enqueue